One-Time Cuts
Great for anyone looking to take a break from mowing their lawn.
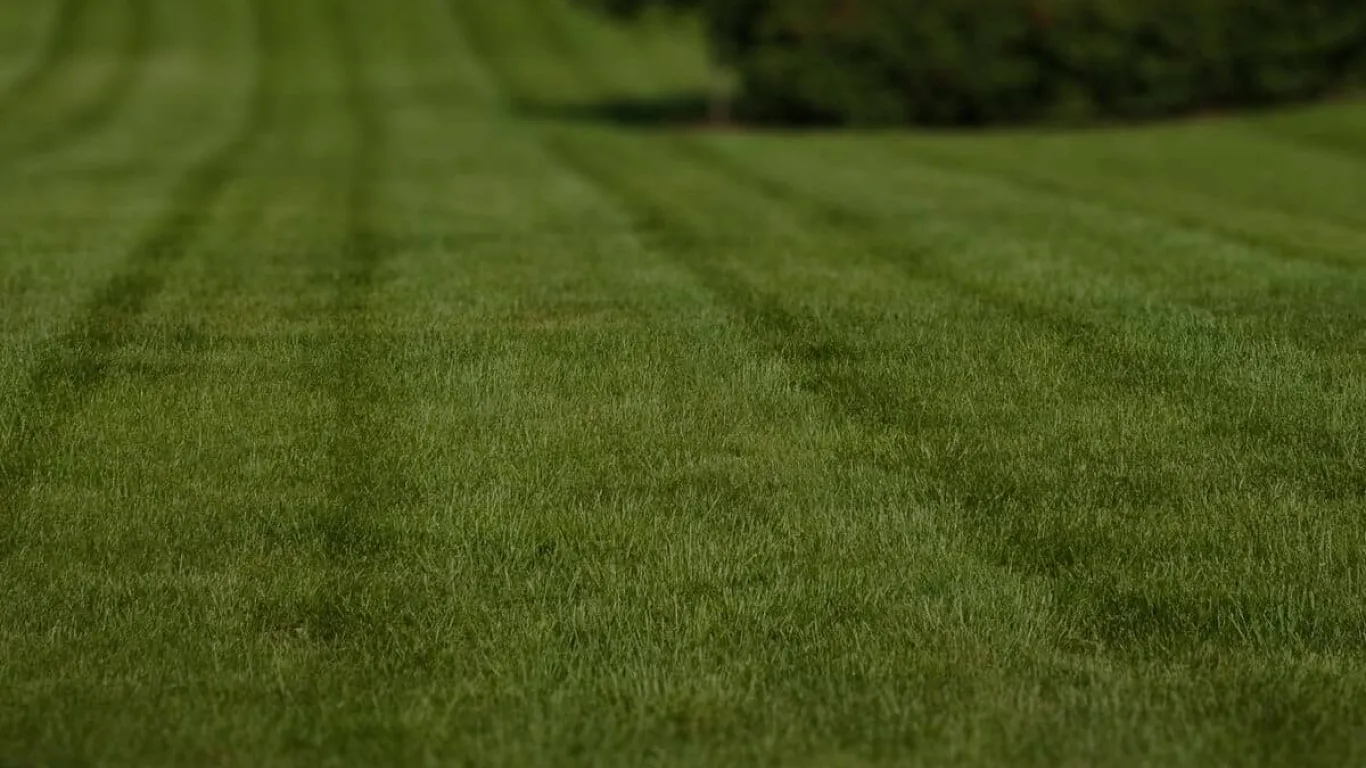


Get Free Lawn Quote in 30 Seconds
Let AI estimate your lawn care price based on local data

With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]

With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]

With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]

With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
Fast, Easy, & Free Quotes

Enter Your Details


Choose a Pro



Book Your Appointment
The GreenPal community provides

One-Time Cuts
Great for anyone looking to take a break from mowing their lawn.

Recurring Service
Perfect for those in need of weekly, bi-weekly or monthly cuts.
Weekly customers save up to 30%

One-Time Cuts
Great for anyone looking to take a break from mowing their lawn.

Recurring Service
Perfect for those in need of weekly, bi-weekly or monthly cuts.




 Read their reviews and choose with confidence
Read their reviews and choose with confidence
 Hire with ease & relax
Hire with ease & relax
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]


Lemont
Florissant
Buffalo
Chicago
Lee’s Summit
Blue Springs
60440

With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
What is now Illinois was inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous cultures, including the advanced civilization centered in the Cahokia region. The French were the first Europeans to arrive, settling near the Mississippi River in the 17th century, in the region they called Illinois Country, part of the sprawling colony of New France. Following U.S. independence in 1783, American settlers began arriving from Kentucky via the Ohio River, and the population grew from south to north. Illinois was part of the United States' oldest territory, the Northwest Territory, and in 1818 it achieved statehood. The Erie Canal brought increased commercial activity in the Great Lakes, and the small settlement of Chicago became one of the fastest growing cities in the world, benefiting from its location as one of the few natural harbors in south-western Lake Michigan.[8] The invention of the self-scouring steel plow by Illinoian John Deere turned the state's rich prairie into some of the world's most productive and valuable farmland, attracting immigrant farmers from Germany and Sweden. In the mid 19th century, the Illinois and Michigan Canal and a sprawling railroad network greatly facilitated trade, commerce, and settlement, making the state a transportation hub for the nation.[9]
With Chicago in the northeast, small industrial cities and immense farmland in the north and center, and natural resources such as coal, timber, and petroleum in the south, Illinois has a highly diverse economy. Owing to its central location and geography, the state is a major transportation hub: the Port of Chicago enjoys access to the Atlantic Ocean through the Great Lakes and Saint Lawrence Seaway, and to the Gulf of Mexico from the Mississippi River via the Illinois Waterway. Additionally, the Mississippi, Ohio, and Wabash rivers form parts of the state's boundaries. Chicago's O'Hare International Airport has been among the world's ten busiest airports for decades. Described as a microcosm of the entire United States,[7] Illinois has long been considered a bellwether in social, cultural, and political terms.[7]
November in Boolingbrook means it's time for fall cleanup! While the total jobs completed in the last 60 days is at 0, homeowners are gearing up to prepare their yards for the upcoming winter months. Now is the perfect time to schedule those final lawn mowing and leaf removal services.
Although there are currently no active vendors listed in the area, GreenPal is your go-to source for connecting with local lawn pros when they become available. Popular services for this time of year include leaf removal and yard prep. We serve neighborhoods like Kids Empire Bolingbrook, Johansen Farm Neighborhood Park, and Winston Village Association.
With an average response time within 1 hour when vendors are active, you can quickly get your lawn service needs addressed. While the repeat customer rate is currently at 0%, you can always check for new reviews to find the best fit for your lawn care near me.
Explore top-rated lawn care in Boolingbrook and book your next mowing today through GreenPal.
Expert tips and advice tailored to your area
I am testing the alt text functionality for the images.Is it generated automatically when images are uploaded or...

Each week, thousands of customers across the U.S. trust our network of professional landscapers. In Boolingbrook, IL, we evaluate lawn care companies based on five key performance areas: customer satisfaction, service quality, punctuality, job volume, and responsiveness. This approach helps us identify and highlight the top-performing lawn mowing services in the area

Save Time, Save Money, Book a great local landscaping service in Boolingbrook now with GreenPal.